AI Route Optimization Software in 2026: How Machine Learning Is Saving Fleets 15–25% on Fuel and Cutting Carbon

The route optimization software market is projected to reach $12.59 billion in 2026, growing at a 14.52% CAGR toward $42.65 billion by 2035. Behind that growth is a simple reality: fleets running AI-optimized routes are saving 15–25% on fuel while their competitors burn cash on static routing that ignores real-time conditions.
The Problem With Static Routing
Traditional route planning treats delivery sequences as a solved problem — plug in addresses, calculate shortest distances, hand drivers a manifest. But logistics doesn't operate in a vacuum. Traffic patterns shift hourly. Weather closes roads. Customer time windows change. A driver's tenth stop might cancel while three new pickups appear.
Static routing engines recalculate once, typically the night before. By 10 AM, the plan is already obsolete. The result: excess miles, unnecessary fuel burn, missed delivery windows, and frustrated customers.
How Machine Learning Changes the Equation
AI route optimization platforms ingest real-time data streams — live traffic, weather forecasts, vehicle telemetry, historical delivery patterns, and customer availability — to continuously recalculate optimal routes throughout the day. Unlike rules-based systems that optimize for a single variable (usually distance), ML models balance dozens of constraints simultaneously: fuel efficiency, driver hours-of-service, vehicle capacity, delivery priority, and emissions targets.
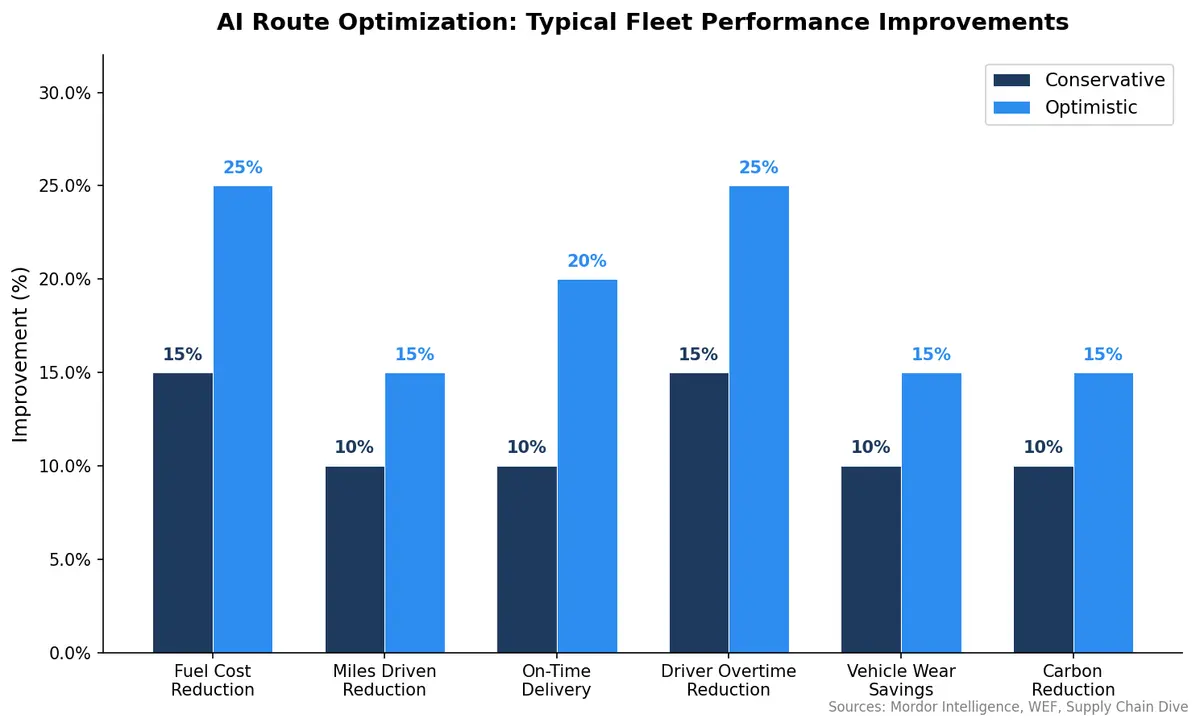
The difference is measurable. According to Mordor Intelligence, the route optimization software market is expanding at 14.7% annually as fleets recognize that AI-driven routing consistently outperforms manual and static methods. Documented fuel savings from AI route optimization range from 10–25%, with most fleets achieving 15–20% reductions through shorter routes, reduced idling, traffic avoidance, and optimized stop sequences.
A World Economic Forum report found that AI can create a 7% reduction in logistics emissions through route optimization and efficient asset management alone — before accounting for mode-shifting or electrification strategies.
The UPS ORION Benchmark
No discussion of AI route optimization is complete without UPS's ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation) system — arguably the most successful deployment in logistics history.
ORION processes 250,000 routing requests per day across UPS's global delivery network. The results speak for themselves: 100 million fewer miles driven annually, translating to $300–400 million in annual cost savings and 100,000 metric tons of CO₂ eliminated. The dynamic ORION upgrade reduced individual driver routes by two to four miles on average, building on an earlier eight-mile-per-driver reduction.
What makes ORION instructive isn't just the scale — it's the methodology. UPS didn't simply overlay AI on existing routes. They rebuilt the routing architecture to treat every delivery day as a unique optimization problem, incorporating real-time package flow data, driver behavior patterns, and dynamic customer windows.
As Supply Chain Dive reported, the dynamic system now covers 97% of UPS's van fleet, providing drivers with reoptimized routes based on changing conditions and turn-by-turn directions to reduce excess miles.
Real-Time vs. Static: Where the Savings Come From
The fuel savings from AI routing break down into five categories:
1. Distance Reduction (5–12% savings) ML algorithms find shorter paths by evaluating millions of route permutations that human planners and basic software miss. For a 50-vehicle fleet averaging 60,000 miles per vehicle per year, a 15% mileage reduction eliminates 450,000 miles annually — saving roughly $247,500 in variable costs at $0.55 per mile.
2. Idle Time Elimination (3–7% savings) AI routing accounts for real-time traffic congestion, rerouting drivers around bottlenecks rather than having them sit in gridlock burning fuel at zero productivity.
3. Stop Sequence Optimization (2–5% savings) The order in which a driver visits stops matters enormously. Optimizing for right-hand turns (reducing left-turn wait times), clustering nearby stops, and sequencing by time window constraints compounds into significant fuel reductions.
4. Load Balancing (2–4% savings) ML models distribute deliveries across vehicles to minimize total fleet miles rather than optimizing individual trucks. This fleet-level optimization often produces counterintuitive solutions that outperform truck-by-truck planning.
5. Predictive Adjustments (1–3% savings) Historical data on seasonal traffic patterns, construction zones, and weather-related delays allows AI systems to proactively avoid problems before they occur.
Integration With TMS Platforms
Route optimization doesn't exist in isolation. The real value emerges when AI routing connects to broader transportation management systems, creating a feedback loop between planning, execution, and analysis.
Modern TMS platforms integrate route optimization data with:
- Order management — automatically batching orders into optimal delivery waves
- Carrier selection — matching route requirements to vehicle capabilities and driver certifications
- Customer communication — providing accurate ETAs based on real-time route calculations
- Emissions reporting — tracking actual vs. planned fuel consumption and carbon output per route
- Cost allocation — attributing transportation costs to specific customers, lanes, or service levels
This integration transforms route optimization from a standalone tool into a strategic capability that improves every downstream logistics decision.
The Carbon Reduction Imperative
With Scope 3 emissions reporting requirements tightening globally, AI route optimization has become a compliance tool as much as a cost-saving one. Fleets that can demonstrate measurable emissions reductions through optimized routing gain competitive advantages in RFP processes where shippers increasingly weight sustainability metrics.
AI-optimized routing cuts fuel consumption by 10–15% on average, directly reducing fleet carbon emissions. For a mid-size fleet burning 500,000 gallons of diesel annually, a 15% reduction eliminates 75,000 gallons — equivalent to roughly 760 metric tons of CO₂.
ROI: The Numbers That Matter
For fleet operators evaluating AI route optimization software, the ROI calculation is straightforward:
Most fleets achieve full payback within 6–12 months of deployment, with ongoing annual savings that compound as the ML models improve with more operational data.
What Comes Next
The route optimization market is moving toward fully autonomous logistics orchestration — where AI doesn't just optimize routes but makes end-to-end decisions about which orders to accept, which vehicles to dispatch, and when to dynamically reroute based on real-time demand signals. The platforms winning in 2026 are those that treat route optimization not as a feature but as the foundation of intelligent transportation management.
Ready to integrate AI-powered route optimization into your logistics operations? Contact CXTMS for a demo and see how intelligent routing can cut your fleet costs by 15–25%.


