Robotics-as-a-Service Is Reshaping Warehouse Economics: Why Shippers Are Renting Robots Instead of Buying Them

The warehouse automation market is booming—valued at $8.75 billion in 2026—but most mid-size shippers can't afford the $500,000+ price tag of a traditional robot deployment. Enter Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS), the subscription model that's turning warehouse automation from a capital expense into a monthly operating cost, and fundamentally changing who can afford to automate.
The CapEx Problem That Created RaaS
Warehouse automation has never been more necessary. DHL now runs autonomous mobile robots across 95% of its global warehouses, with item-picking robots increasing units picked per hour by 30%. UPS processes 68% of its U.S. volume through automated facilities. FedEx estimates the global warehouse automation market will exceed $51 billion by 2030.
But these are billion-dollar companies. For a regional 3PL or mid-size shipper, purchasing an autonomous mobile robot (AMR) fleet means committing $300,000 to $1 million upfront—plus integration, maintenance, and the risk that the technology becomes obsolete within three years.
RaaS eliminates that barrier. Instead of buying robots, companies subscribe to them, paying a monthly fee that typically includes the hardware, software, maintenance, and upgrades.
How the RaaS Model Works
Think of RaaS as the SaaS of physical automation. Just as companies stopped buying servers and moved to cloud computing, warehouses are moving from owning robots to subscribing to robotic capabilities.
A typical RaaS deployment works like this:
- Pay-per-pick or pay-per-hour: Costs scale directly with throughput, so you only pay for what you use
- Bundled maintenance: The provider handles repairs, software updates, and hardware refreshes
- Flexible scaling: Add robots during peak season, return them when volume drops
- Rapid deployment: Most RaaS providers can deploy robots in weeks, not months
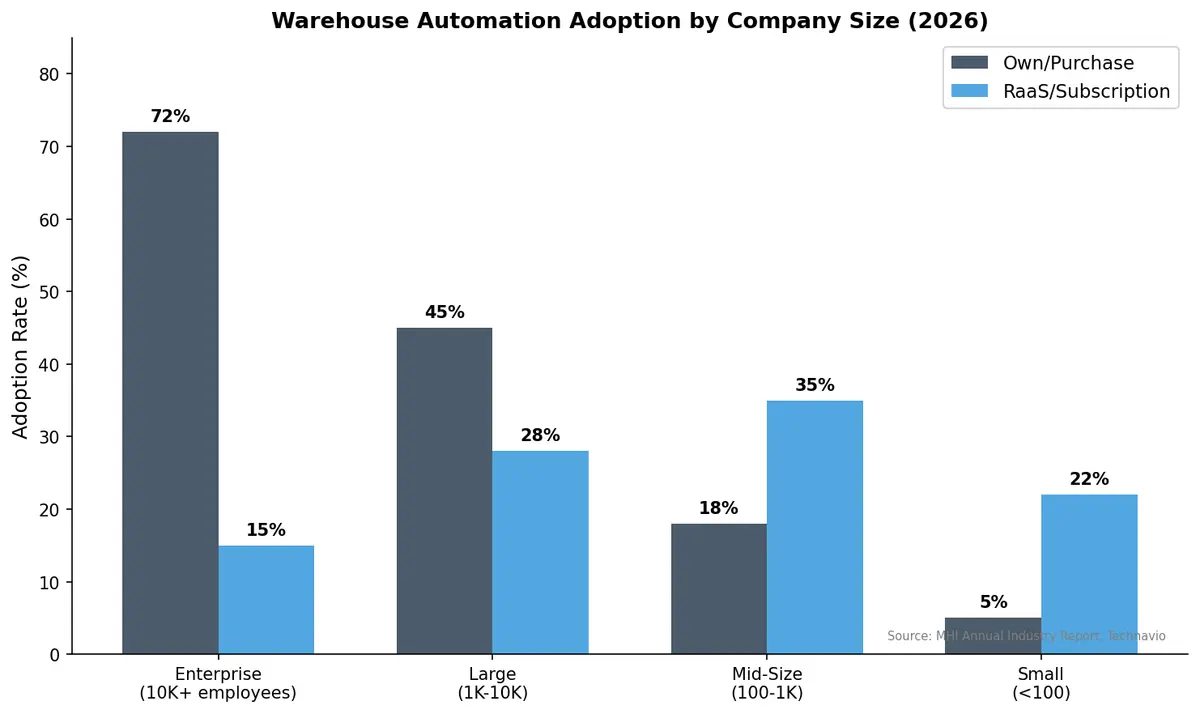
As Modern Materials Handling's 2026 automation study confirms, warehouse automation adoption continues to tick upward, with AGVs and palletizing robotics gaining traction across facilities of all sizes. The RaaS market is growing at a 23.47% CAGR, projected to add $2.5 billion in value between 2024 and 2028, according to Technavio. Customized RaaS solutions are expected to account for nearly 40% of the market by 2026.
The Economics: Buy vs. Rent
The financial case for RaaS is most compelling for operations with seasonal variability or rapid growth.
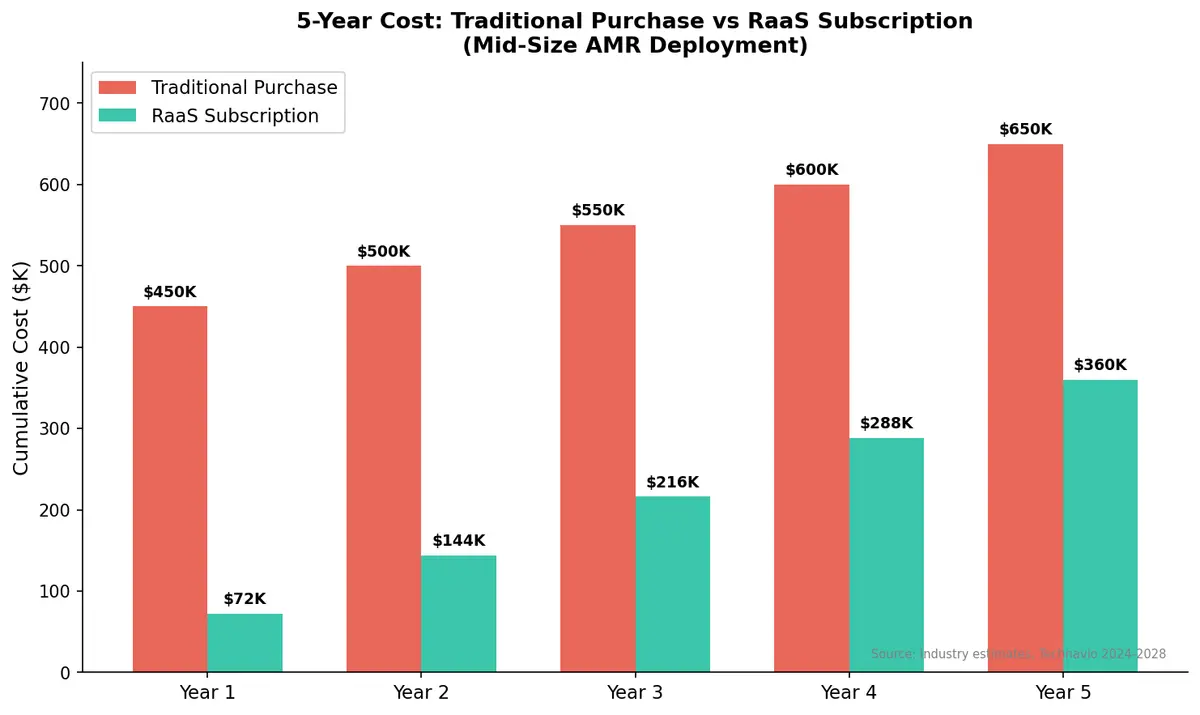
Traditional purchase:
- Upfront cost: $150,000–$500,000+ per robot system
- Integration and installation: $50,000–$200,000
- Annual maintenance: 10–15% of purchase price
- Technology refresh cycle: 3–5 years
- Total 5-year cost: $250,000–$875,000 per system
RaaS subscription:
- Monthly fee: $2,000–$10,000 per robot (depending on capability)
- No upfront capital expenditure
- Maintenance included
- Technology upgrades included
- Total 5-year cost: $120,000–$600,000 per system
For seasonal shippers—think retail fulfillment centers that triple their volume in Q4—the math is even more favorable. Leasing additional robots for three months costs a fraction of purchasing units that sit idle for nine months.
Why 2026 Is the Inflection Year
Three forces are converging to make RaaS mainstream in 2026:
1. The labor crisis is accelerating. UPS has cut more than 75,000 jobs over the past year while simultaneously automating 127 buildings. DHL's global head of digital transformation, Tim Tetzlaff, told CNBC that finding labor near distribution centers is "typically very tough." Automation isn't replacing workers—it's filling roles that can't be staffed.
2. Robot capabilities have matured. DHL's AMRs now unload containers at 650 cases per hour. Autonomous forklifts deliver a 20% efficiency increase. FedEx's partnership with Berkshire Grey has produced fully autonomous trailer unloaders. These aren't experimental—they're production-grade.
3. The subscription economy has trained buyers. Procurement teams that already manage SaaS licenses, cloud infrastructure, and equipment leases understand subscription models intuitively. RaaS fits neatly into existing OpEx budgets without board-level capital approval.
What to Look for in a RaaS Provider
Not all RaaS offerings are equal. Key evaluation criteria include:
- Integration capabilities: Can the robots connect with your existing WMS and TMS? API-first architecture is essential
- Scalability terms: How quickly can you add or return units? What are the minimum commitment periods?
- Performance SLAs: What throughput guarantees does the provider offer? How is downtime handled?
- Data ownership: Who owns the operational data the robots generate? This data is valuable for process optimization
- Technology roadmap: How often does the provider refresh hardware? Are software updates included?
How CXTMS Integrates with Automated Warehouses
Whether you buy or rent your warehouse robots, the operational data they generate needs to flow into your transportation management system. CXTMS connects with automated warehouse systems through standardized APIs, enabling:
- Real-time inventory visibility across automated and manual facilities
- Dynamic load planning based on actual pick-and-pack throughput
- Automated shipping triggers when orders complete robotic processing
- Unified analytics combining warehouse automation metrics with transportation KPIs
The shift from CapEx to OpEx in warehouse automation mirrors the broader trend toward flexible, data-driven logistics operations. Companies that can integrate their RaaS deployments with intelligent TMS platforms gain a compounding advantage—lower automation costs, faster fulfillment, and the operational agility to scale with demand.
Exploring warehouse automation integration? Contact CXTMS for a demo of how our platform connects with robotic fulfillment systems.


